NEW STUDY IN PRESS! CLAPPING IN TIME PARALLELS LITERACY & CALLS UPON OVERLAPPING NEURAL MECHANISMS IN EARLY READER
“Clapping in time parallels literacy and calls upon overlapping neural mechanisms in early readers” was just accepted by the Ann NY Acad Sci. The data are a strong endorsement of the connection between IM, literacy and underlying biological mechanisms.
CLAPPING IN TIME PARALLELS LITERACY & CALLS UPON OVERLAPPING NEURAL MECHANISMS IN EARLY READERS CLAPPING IN TIME PARALLELS LITERACY & CALLS UPON OVERLAPPING NEURAL MECHANISMS IN EARLY READERS
Silvia Bonacina, Jennifer Krizman, Travis White-Schwoch & Nina Kraus Published in Annals of The New York Academy of Sciences, 2018
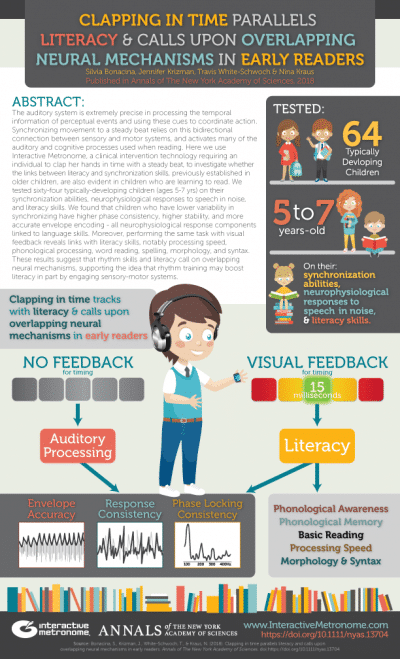
ABSTRACT: The auditory system is extremely precise in processing the temporal information of perceptual events and using these cues to coordinate action. Synchronizing movement to a steady beat relies on this bidirectional connection between sensory and motor systems, and activates many of the auditory and cognitive processes used when reading. Here we use Interactive Metronome, a clinical intervention technology requiring an individual to clap her hands in time with a steady beat, to investigate whether the links between literacy and synchronization skills, previously established in older children, are also evident in children who are learning to read. We tested sixty-four typically-developing children (ages 5-7 yrs) on their synchronization abilities, neurophysiological responses to speech in noise, and literacy skills. We found that children who have lower variability in synchronizing have higher phase consistency, higher stability, and more accurate envelope encoding – all neurophysiological response components linked to language skills. Moreover, performing the same task with visual feedback reveals links with literacy skills, notably processing speed, phonological processing, word reading, spelling, morphology, and syntax. These results suggest that rhythm skills and literacy call on overlapping neural mechanisms, supporting the idea that rhythm training may boost literacy in part by engaging sensory-motor systems.
Download the Infographic here!
Read the Full Paper here!
